- This topic is empty.
-
CreatorTopic
-
October 26, 2024 at 2:03 pm #7515::
Understanding user behavior is crucial for enhancing the e-commerce shopping experience, boosting customer satisfaction, and driving conversions. User journey mapping is an effective tool that visualizes the various stages customers go through while interacting with a brand, from awareness to purchase and post-purchase engagement.
1. Understanding the Basics of User Journey Mapping
User journey mapping is the process of creating a visual representation of the steps a user takes while interacting with an e-commerce platform. It highlights user motivations, pain points, and engagement opportunities, making it easier for businesses to improve UX, streamline sales funnels, and ultimately increase conversions.

2. Benefits of User Journey Mapping in E-Commerce
Mapping out a user’s journey provides several advantages:
- Improved User Experience: Identifies friction points in the shopping journey that may need improvement.
- Enhanced Customer Retention: By addressing pain points, you create a smoother experience that keeps customers coming back.
- Targeted Marketing: Helps tailor marketing efforts to specific user behaviors and touchpoints.
- Conversion Rate Optimization: Pinpoints areas where conversions drop, enabling focused improvements.
3. Essential Steps to Create a User Journey Map
- Define Customer Personas: Begin by understanding your audience through data on demographics, preferences, purchase habits, and motivations. E-commerce personas might include first-time shoppers, return customers, and cart-abandoners, each with unique pain points and journeys.
- Identify Key Touchpoints: Recognize the various touchpoints customers interact with, including ads, social media, website pages, and emails. For example, in e-commerce, this could include product pages, reviews, checkout, and post-purchase communication.
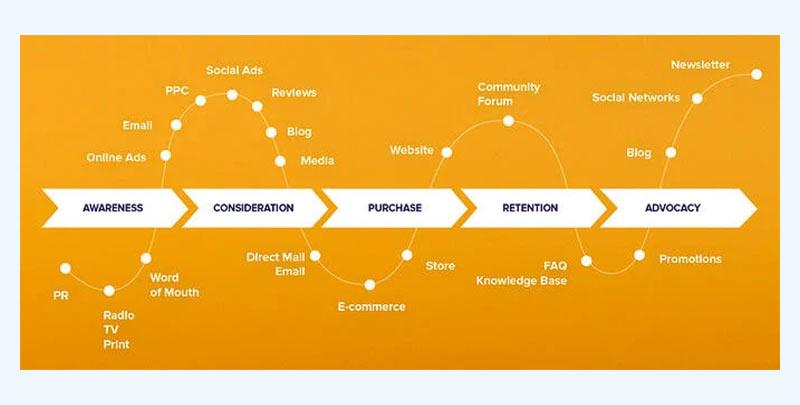
- Map Out Stages of the Journey:
- Awareness: User discovers the brand through ads, search engines, or social media.
- Consideration: User explores product pages, reads reviews, or adds items to the cart.
- Conversion: User goes through checkout and finalizes the purchase.
- Post-Purchase: User receives order confirmation, follows up with customer service, or reviews the product.
- Retention: User returns for repeat purchases, uses loyalty programs, or engages in promotional offers.
- Analyze User Emotions: Emotion plays a big role in the e-commerce journey. Use data to determine how users feel at each stage. For instance, an abandoned cart might indicate frustration, while repeat purchases suggest satisfaction and loyalty.
- Highlight Pain Points and Moments of Delight: Address issues that cause friction, such as complex navigation, and emphasize positive interactions, like fast shipping or easy returns.
- Collect and Integrate Feedback: Use customer surveys, reviews, and analytics to continually update the journey map based on real feedback.
4. Key Techniques for E-Commerce Journey Mapping
- Empathy Mapping: A valuable method for understanding user motivations and concerns. Break down what users say, think, do, and feel at each stage to understand their mindset and how they interact with your platform.
- Service Blueprinting: Goes beyond the user’s journey to include internal processes. This technique helps align what happens behind the scenes (like inventory management and customer support) with the user experience, ensuring seamless transactions.
- Time-on-Task Analysis: Helps identify where users spend the most time, which can indicate areas that need refinement. For instance, a lengthy checkout process may suggest an opportunity for simplification.
- Customer Feedback Loop: Collect and implement insights from post-purchase surveys, customer reviews, and direct feedback. This ongoing loop keeps your journey map aligned with actual user experiences.
- Conversion Funnel Analysis: Track how users move from one stage to another, identifying any “leaks” in the funnel where users drop off. For example, if a significant number of users abandon their carts, consider enhancing the checkout UX or adding retargeting campaigns.
- Heatmaps and Click Tracking: Use tools like heatmaps to see where users click and hover most on your site. This data can show what attracts attention (like high-traffic products or offers) and areas that might need UX improvement.
5. Tools for E-Commerce Journey Mapping
- Google Analytics: An essential tool for tracking user behavior, understanding which pages users visit most, and identifying traffic sources.
- Hotjar and Crazy Egg: Excellent for heatmaps and session recordings, giving insight into user navigation patterns.
- Customer Feedback Platforms (like Typeform or SurveyMonkey): Collect qualitative data directly from users at various journey stages to improve understanding of pain points and areas for improvement.
- Adobe XD and Figma: Great for creating detailed, interactive journey maps that help teams visualize user journeys and align on experience improvements.
6. Common Pitfalls and Tips
- Avoiding Complexity: Keep the journey map focused. Too many details can make it challenging to interpret and act upon insights.
- Regular Updates: User behavior evolves, so make sure to update your journey map regularly to reflect new trends and insights.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Effective journey maps require input from multiple departments, including marketing, customer support, and development.
In e-commerce, a well-designed user journey map can make a significant difference in delivering a simple, satisfying shopping experience. By understanding and addressing the specific needs, pain points, and motivations of your users, you’re better positioned to boost loyalty and ultimately drive the success of your online store. Embracing journey mapping as a continuous process rather than a one-time task allows e-commerce brands to stay responsive and adaptable to changing customer expectations.
-
CreatorTopic
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.