- This topic is empty.
-
Topic
-
The UK road sign system is a comprehensive and standardized set of signs designed to convey information to road users quickly and efficiently. These signs play a crucial role in guiding drivers, pedestrians, and cyclists, as well as conveying regulatory information, warnings, and other essential messages.
Features and categories of UK road signs:
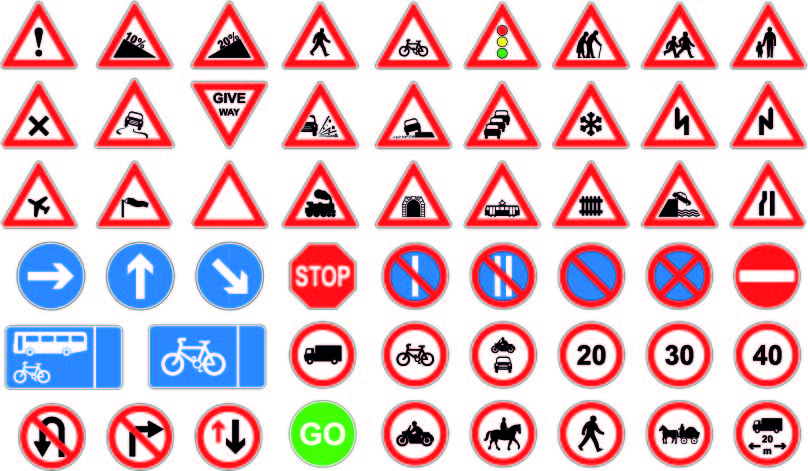
- Regulatory Signs:
- Round Signs: These signs indicate mandatory instructions, such as speed limits, no-entry zones, and the start of controlled parking zones.
- Triangular Signs: Often warning of hazards or providing information on road conditions, such as road narrowing, pedestrian crossings, or intersections.
- Warning Signs:
- Triangular Signs: Alert drivers to potential hazards ahead, such as bends in the road, junctions, or pedestrian crossings.
- Diamond Signs: Used for warnings related to road work, lane closures, or other temporary conditions.
- Informational Signs:
- Rectangular Signs: Convey information about facilities, directions, or services, such as parking areas, tourist attractions, or hospitals.
- Blue Signs: Typically indicate motorway information, including directions to motorway entrances, service areas, and distances to upcoming exits.
- Direction Signs:
- Directional Arrows: Used to guide drivers in specific directions, especially at complex junctions or roundabouts.
- Fingerpost Signs: Common in rural areas, these signs typically display the names of destinations and distances.
- Road Markings:
- In addition to signs, road markings are used to convey information. For example, white lines indicate lanes, yellow lines denote parking restrictions, and zebra crossings are marked with distinctive black and white stripes.
- Speed Limit Signs:
- Circular signs with a red border and a black numeral indicate the maximum speed limit on a particular road.
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Signs:
- Include crossings, cycle lanes, and pedestrian zones to enhance safety for non-motorized road users.
- Variable Message Signs (VMS):
- Electronic signs that can display changing information, such as variable speed limits or real-time traffic updates.
- Low Emission Zone Signs:
- Indicate areas where vehicles must meet specific emission standards to enter.
- Parking Signs:
- Indicate parking restrictions, time limits, and payment requirements in specific areas.
It’s important to note that the design principles introduced by Margaret Calvert and Jock Kinneir in the 1960s have influenced the clarity and uniformity of these signs. The use of standardized colors, shapes, and fonts helps ensure that road signs are easily recognizable and understandable by a diverse range of road users.
Margaret Calvert is a British graphic designer who played a significant role in the development and design of road signs in the United Kingdom. Along with her colleague Jock Kinneir, she was part of the design team responsible for the iconic road sign system introduced in the 1960s. Their work became the foundation for modern road signage in the UK.
In the early 1960s, the UK government established the Worboys Committee, chaired by Sir Walter Worboys, to review and improve road signage. Margaret Calvert, who was then a student at the Chelsea College of Art, collaborated with Jock Kinneir, a design lecturer at the Royal College of Art, to create a new set of road signs based on the committee’s recommendations.
Contributions by Margaret Calvert and Jock Kinneir to the UK road sign system:
- Clear and Simple Design: They focused on creating clear and simple designs that could be easily understood by drivers at a glance. The signs featured bold, uppercase letters and distinctive symbols.
- Unified Typeface (Transport): Calvert designed a new typeface known as “Transport” for the road signs. This typeface was carefully crafted for optimal legibility and visibility, even at high speeds and in adverse weather conditions.
- Color and Shape Coding: The use of specific colors and shapes for different categories of signs helped drivers quickly identify the type of information a sign was conveying. For example, warning signs had a distinctive triangular shape, while regulatory signs were circular.
- Human Factors Consideration: The design team paid attention to human factors and psychology, considering how drivers process information. The clear and consistent design of the signs aimed to reduce confusion and enhance safety.
- Standardization: The work of Calvert and Kinneir laid the foundation for standardization in road signs. The signs they designed became part of the Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions (TSRGD) introduced in 1964.
Margaret Calvert’s contributions to road signage design have had a lasting impact, not only in the UK but also internationally. The design principles she and Kinneir established have influenced the development of road sign systems in various countries. Margaret Calvert is recognized for her significant role in shaping the visual language of road signs and making them an integral part of transportation systems worldwide.
History of UK road signs:
The history of road signs in the United Kingdom can be traced back to the early 20th century when the automobile industry was rapidly growing, and there was a need for standardized road signage to regulate traffic and ensure road safety.
- Early Signs (1920s): In the 1920s, road signs began to appear on UK roads, but there was no standardization, and signs were often homemade. The first signs were simple, with basic symbols and text to convey information to drivers.
- First Standardization (1930s): The first significant attempt at standardizing road signs in the UK occurred in the 1930s. The Ministry of Transport introduced a set of standardized signs in 1933, known as the “Aerodrome Signs,” which featured simple symbols on a blue background. These signs were primarily aimed at guiding drivers to airports.
- The Worboys Committee (1963): As traffic continued to increase, the government recognized the need for a comprehensive system of road signs. In 1963, the Worboys Committee, chaired by Sir Walter Worboys, was established to review and improve road signage in the UK. The committee’s recommendations led to the introduction of the Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions (TSRGD) in 1964.
- The Red Triangle (1970s): One of the significant changes introduced in the 1970s was the use of a red triangle to indicate a warning or caution. This distinctive shape made warning signs more easily recognizable to drivers.
- 1994 Regulations: In 1994, further revisions were made to the TSRGD, bringing about changes to sign designs, colors, and symbols. The objective was to enhance clarity and effectiveness in conveying information to road users.
- Continued Evolution: Since the 1990s, the UK has continued to update and refine its road sign system. New signs have been introduced, and existing ones have been modified to reflect changes in technology, road design, and traffic management.
- European Influence and Brexit: The UK’s road signs have also been influenced by European standards, particularly those established by the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. However, with the UK’s exit from the European Union (Brexit), there may be future developments in road sign standards to reflect the country’s changing relationship with international regulations.


- Regulatory Signs:
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.