- This topic is empty.
-
Topic
-
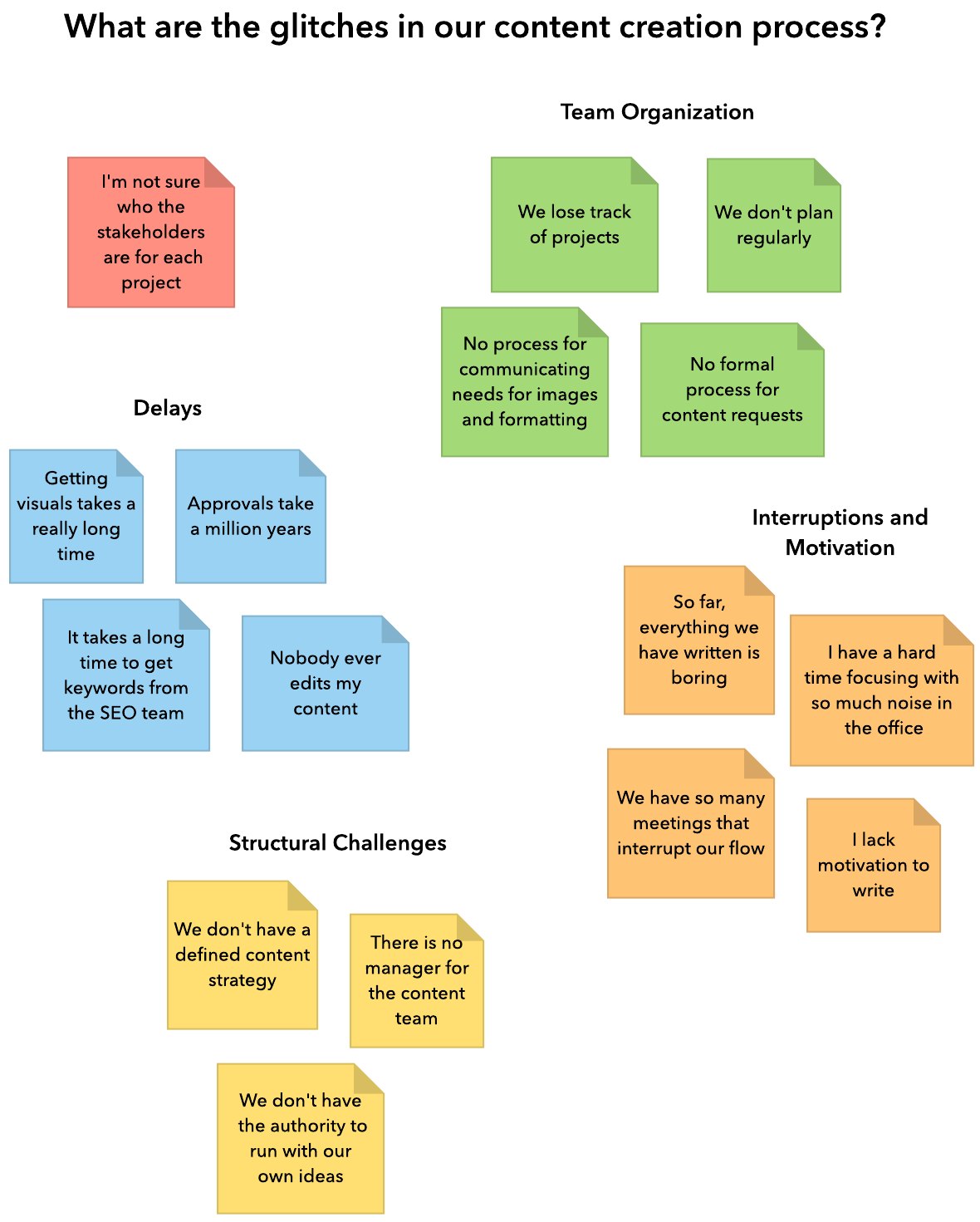
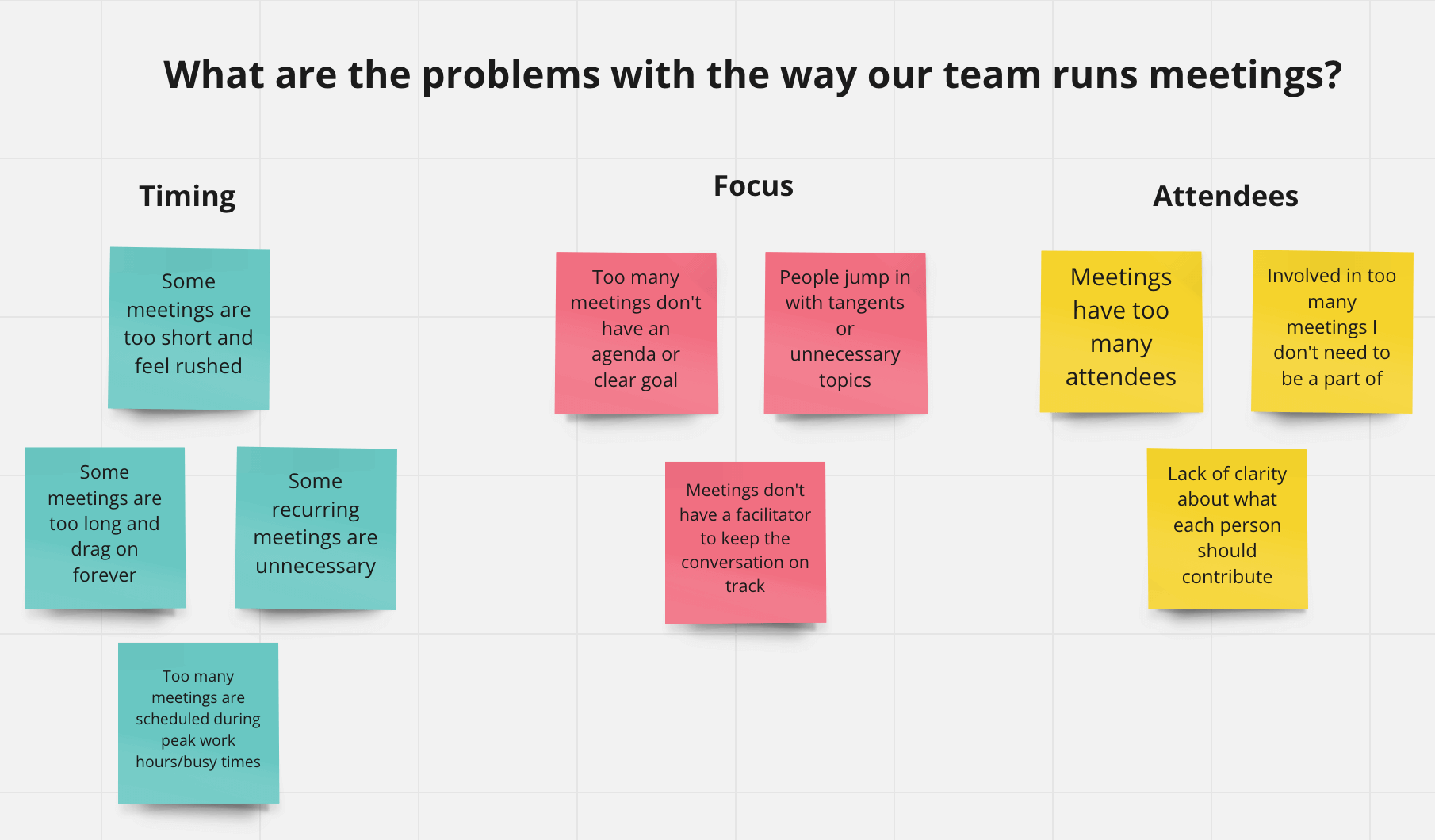
An Affinity Diagram or mapping is a technique used in brainstorming and problem-solving sessions to organize and categorize ideas, opinions, or data. It is also known as the KJ method after its creator, Jiro Kawakita.
The process involves writing down ideas or data on individual sticky notes or cards and then grouping them together into categories based on their similarities or relationships. The categories emerge from the relationships that exist between the ideas or data and can be named based on the common theme that connects them.
It is a useful tool in project management, quality improvement, and team-building exercises. It helps to identify patterns, uncover hidden connections, and provide a visual representation of complex information. It encourages group participation and promotes collaboration among team members, which leads to a shared understanding of the issues and a more effective solution.
Steps:
- Define the problem or issue to be addressed: Clearly state the problem or issue that the team is trying to solve.
- Gather ideas: Write down each idea or thought related to the problem or issue on individual sticky notes or index cards. Encourage everyone to participate and contribute their ideas.
- Group similar ideas: Begin to group the sticky notes or index cards into categories based on similarities or relationships. Look for themes or patterns that emerge.
- Label the categories: Once you have grouped the ideas, give each category a name that reflects the common theme that connects the ideas.
- Review and refine: Step back and review the categories to ensure that they are relevant and make sense. Refine or combine categories as needed.
- Identify next steps: Use the affinity diagram to help generate ideas for next steps or solutions to the problem or issue. Determine the actions that need to be taken to address the problem.
- Communicate and share: Share the results of the affinity diagram with the team and stakeholders. Use it as a tool for discussion and decision-making.
Advantages
- Encourages participation: Encourages participation from all team members and stakeholders. It allows everyone to contribute their ideas and opinions, leading to a more diverse and comprehensive set of ideas.
- Organizes information: The process of creating an affinity diagram or map helps to organize and categorize information. It provides a visual representation of complex information, making it easier to understand and analyze.
- Identifies patterns and relationships: By grouping similar ideas or data together, it can identify patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent. This can lead to new insights and ideas.
- Promotes collaboration: Promotes collaboration among team members. It encourages discussion and debate, leading to a shared understanding of the problem or issue and a more effective solution.
- Generates ideas for next steps: Help generate ideas for next steps or solutions to the problem. It provides a starting point for further discussion and decision-making.
- Cost-effective: Cost-effective tool that can be used in a variety of settings. It requires only sticky notes or index cards and a space to display them.
Disadvantages
- Time-consuming: Can be a time-consuming process, particularly if there are a large number of ideas or data to organize.
- Subjectivity: The process of grouping ideas and data into categories is subjective, and different people may group them differently. This can lead to disagreements or biases.
- Lack of structure: Provides a framework for organizing information, but it may not provide a structured approach to problem-solving or decision-making. It requires additional steps to determine the best course of action.
- Limited scope: May be limited in scope, depending on the problem or issue being addressed. It may not be suitable for more complex or technical issues that require specialized expertise.
- Over-reliance on consensus: Encourages collaboration and consensus-building, but this may not always be possible or desirable. It may be more effective to have a designated decision-maker or expert provide guidance.


- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.